

Legend has it that back in the early 1990s, IBM was demonstrating command-line voice recognition software when a smart aleck in the audience hollered “Control Alt Delete”! At the time, as IBM PC aficionados recall, that sequence of keystrokes rebooted the PC (today it gives PC users a few options). The computer shut down, the audience chuckled, and the presenter, who hadn’t anticipated such a situation, frowned.
The ability to communicate via a language (sign, spoken, written, etc.) is perhaps as old as human existence itself and sets us humans apart from other species. However, getting machines and computers to perceive and understand human language, a long-time pursuit of scientists, has met with limited success.
Machines haven’t been able to fully crack it because of the very nature of language and the lack of viable machine learning methods. Semantics and word syntax, their context in a sentence, grammar, diction, meaning, intent, and sentiment offer an extremely complex set of problems for a computer to solve.
It is natural for a human brain to learn as it evolves from an infant to adulthood. Our brains are hard-wired to be extremely efficient in learning, understanding, and using languages to communicate. And we do it consuming only a fraction of the energy required by today’s computers to train comparable AI models.
We have come a long way since ELIZA, a dumb rules-based and scripted chatbot computer program, was created in the mid-1960s at the MIT AI Lab. ELIZA simulated a Rogerian psychotherapist and mimicked humanlike conversations—a noncontextual attempt at human-computer interaction to solve psychological disorders.
Even today, most chatbots are primarily rules-based, rigid systems that have well-defined categories and sequences to address specific human queries. They are not conversational, capable only of one-time responses—one reason chatbots sometimes get stuck repeating responses, which leads to unresolved problems, escalation to a human agent, repeated information, broken journeys, and increased frustration, plummeting customer satisfaction (CSAT) and Net Promoter Score (NPS) results, and loss of customers.
Yet companies have woken up to the value of “conversational commerce.” Easy conversations create customer brand affinity and loyalty, enabling companies to grow sales, reduce customer-acquisition costs, and focus on lifeterm value (LTV).
In the early 2010s, an abundance of inexpensive computing horsepower and advancements in conversational AI algorithms pushed the limits of ways machines could mimic the human brain. Examples include Apple’s Siri, Microsoft’s Cortana, Amazon’s Alexa, Google’s Assistant, and several similar applications.
More recently, Google’s groundbreaking research work on transformers led to the open-source neural network (NN)-based technique for natural language processing (NLP) pretraining called BERT. BERT looked at the full context of a word, enabling machines to understand the real intent behind conversational searches.
Google used some brute-force methods—such as using 16 Cloud TPU v2 devices to hardware accelerate the training—along with 350 million internal parameters in the NN to train on a 3.3 billion-word data set culled from Wikipedia. The research enabled the capacity to build large natural language machine learning (ML) models, leading to the gargantuan GPT-3 language model: 175 billion ML parameters, trained on 500 billion words, from OpenAI in 2020. Just to get a sense of 500 billon words, imagine hearing 100 words per minute—it would take about 10,000 years of continuous speech to get to 500 billion!
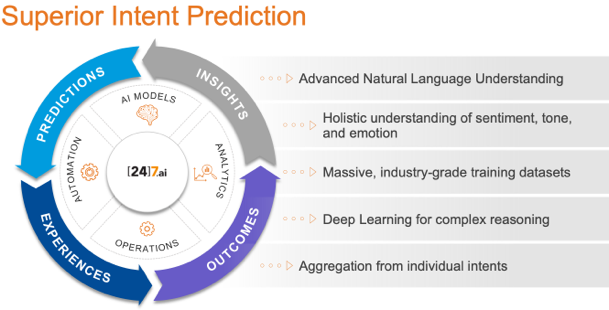
Conversational AI, with its underlying NLP, natural language understanding (NLU), and natural language generation (NLG) technologies, brought together a range of advanced capabilities such as an omnichannel user interface, contextual awareness, language processing, response generation, intent management, exception/escalation management, advanced analytics, and integration with other business applications.
We humans are extremely conversational, interactive, and different from one another in how we communicate and respond to situations. To solve these complexities, conversational AI provides a set of foundational technologies for developing intelligent chatbots, virtual agents, automated messaging systems, agent-assisting bots, FAQ bots, virtual assistants, etc. across multiple channels and use cases. Conversational AI endows these applications with cognitive capabilities to understand human dialogue variance and navigate business systems to resolve customer issues. It handles imprecise communication, understands a person’s intent, disambiguates vague and confusing requests, and brings off-tangent and divergent conversations back on track. Conversational AI shines in its ability to handle text- or voice-based communication variance, delivering successful outcomes and positive customer experiences.
Over the past few years, conversational AI has matured significantly to make a massive impact in applications that typically have used noncontextual, rules-based software to bridge the communication gap between computers and human interaction. As we become more and more digitally savvy citizens, we increasingly turn to our digital devices and channels for solving everything in our day-to-day lives. Conversational AI promises to be the key to unlock tremendous business value resulting from improved customer delight, experiences, and outcomes.
It’s not easy to deliver a smooth customer experience when managing multiple bot systems, vendors, and workflows across multiple platforms. Training agents on multiple consoles can lead to compromising customer data and privacy, not to mention wasted cost and time.
[24]7 Conversations™, our conversational AI platform, and the underlying AIVA conversational technology combines AI with human insight, enabling users to predict and resolve consumer queries quickly and efficiently. Users build bots for messaging, web, mobile, and IVR under one, unified UI and deploy them across all or any channels. Whether you’re building straightforward FAQ-type content or sophisticated conversations involving multiple intents, everything you need is right there at your fingertips.
To learn more about [24]7.ai conversational AI technology, AI chatbot products, and use cases, please check out the following: